Improved vibration generated from hot forging machines (air-drop hammers) used in the factory!
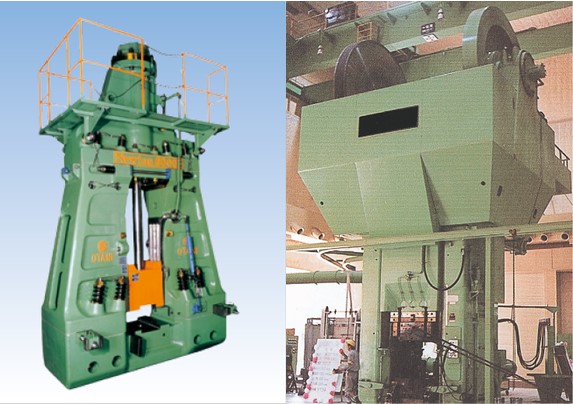
Forging machines that perform metal processing generate very large impact forces during the forming process, and the resulting vibration often affects the surrounding environment. Therefore, it is common practice to support the forging machine with a vibration isolator to isolate vibration from the surrounding ground. This case study introduces the introduction of Yacmo's air spring type vibration isolators.
issue
In the forging process of the air-drop hammer, the ram (lower part of the piston rod in the center of the machine) and the upper die operating section are struck against heated material placed on the lower stand. This is a mechanized version of the manual forging process, and the repetitive striking of the ram, which can be several to several dozen tons, generates extremely large vibrations. To reduce the vibration transmitted to the surrounding ground, it is effective to support the machine with elastic materials to isolate the vibration.
At a certain factory, one additional air-drop hammer was installed, and it began to generate more vibration than ever before. Table 1 shows the specifications of the additional air-drop hammer, and Table 2 and Figures 1 through 3 show the results of vibration measurements. The vibration level was 58 dB at the site boundary, exceeding 55 dB, which is considered to be the level at which people begin to feel vibrations. In response to these results, the plant decided to implement vibration countermeasures to reduce the impact of vibration on neighboring residences and to improve the plant's internal environment. The target value after the countermeasures was set below 55 dB, which is the lowest vibration regulation value in the vicinity of the area (Table 3). In addition to the additional forging machine, another air-drop hammer is in operation at this plant, and since an air-spring type vibration isolator had already been installed and was demonstrating good vibration isolation performance, we asked the client to consider an air-spring type vibration isolator for this plant as well.
Table 1. air-drop hammer machine specifications
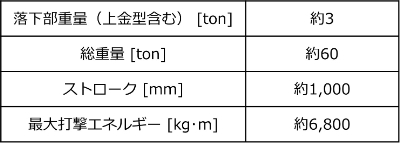
Table 2: Vibration levels during forging machine operation
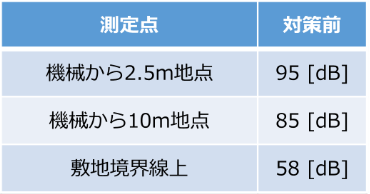
Table 3: Vibration Regulation Standards for Specified Factories, etc. in the Vicinity of the Area
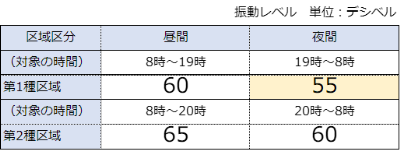
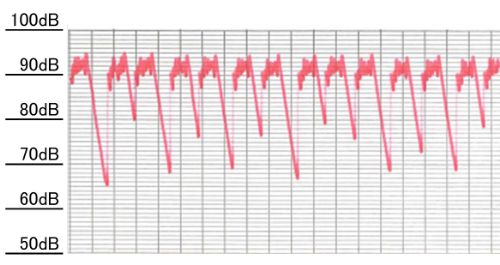
Figure 1: Vibration level time history waveform (2.5 m from machine) before countermeasures
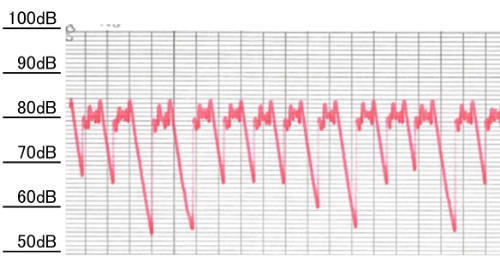
Figure 2: Vibration level time history waveform (10 m from machine) before countermeasures
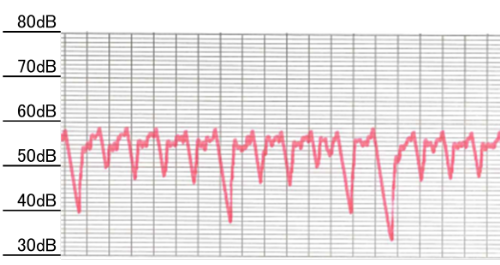
Figure 3 Vibration level time history waveform (on site boundary) before countermeasures
counter-measure
First, a frequency analysis of the measured data was performed in order to understand the vibration characteristics being generated. As a result, it was found that there were large vibrations in the vicinity of the machine in the 12.5 to 20 Hz range and in the 8 to 12.5 Hz range at the site boundary. As a result, a natural frequency of 4 Hz or lower was desirable, and it was decided to take anti-vibration measures using an air-spring system (for a detailed explanation of the concept, please refer to the "Trivia" section here).'TheTrivia: What is vibration isolation?'-' (used in place of '-')(See Section 2.1.2.).
Before actual measures were taken, the effect of vibration reduction by vibration isolation and the machine amplitude were studied for prediction.
The predicted results were a vibration reduction effect of 10 dB or more at each measurement point (Table 4) and a displacement of approximately 17 mm (Figure 4) at the time of impact. Based on these results, it was confirmed that the vibration reduction effect was sufficient to meet the target values and that the displacement at the time of impact would not interfere with workability.
Table 4: Vibration levels during forging machine operation (predicted values after countermeasures)
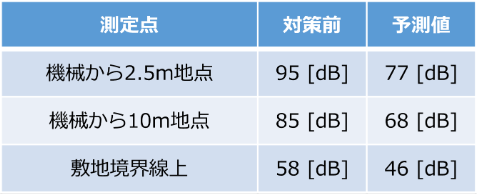
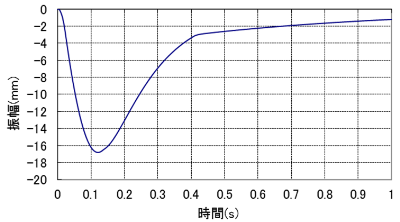
Figure 4: Descent during blow after vibration isolation (predicted)
The study is based on the impact force of the blow, and does not take into account the recoil of the ram swinging up, etc.

Figure 5: Exterior view of anti-vibration mount

Figure 6: Appearance of oil damper

Figure 7: Oil damper appearance (left) and air spring appearance (right)
Table 5: Basic Specifications of Vibration Isolators
result
After installation of the vibration isolators, vibration levels were measured to verify their effectiveness (Table 6, Figures 8-10).
The vibration reduction effect was as predicted (or higher) from the machine's immediate vicinity to the site boundary point, and the vibration level at the site boundary was 44 dB, which was confirmed to satisfy the target value of 55 dB. The vibration level of 44 dB is a level that most people would not feel, and the vibration environment was greatly improved by this measure.
Table 6: Vibration levels during forging machine operation (after countermeasures)
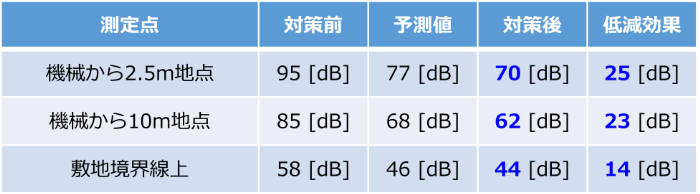

Figure 8: Vibration level time history waveform after countermeasures (2.5 m from machine)

Figure 9: Vibration level time history waveform after countermeasures (10 m from machine)

Figure 10 Vibration level time history waveform (on site boundary) before countermeasures
Related Pages
- Trivia] What is Vibration Isolation? Take measures to prevent machine vibration at the source of the vibration.
- Trivia] Basic Knowledge of Vibration Suppression - What is the difference between "anti-vibration," "vibration isolation," and "vibration suppression"? ~Vibration Isolation
- Product Information] Air Springs
- Case Study] Improvement of floor shaking problem caused by a press machine in a factory
Related Content
- Yacmo's Vibration Prevention Map by Usage Scenario
- Technical Column] Countermeasures for Vibration Problems Caused by Production Equipment Machinery and Examples of Improvements
- Technical Column] Types and Features of Measures to Reduce Floor Swaying Caused by Walking and Machinery
- Webinar Video] Countermeasures for Mechanical Vibration Problems Caused by Production Equipment and Examples of Improvements
