Buildings sway due to traffic vibration on main roads! Ultra-thin vibration control system requires no large-scale construction work!

Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/yacmo/yacmo.co.jp/public_html/wp-content/themes/yacmo/single-achievements.php on line 24
Warning: Attempt to read property "name" on null in /home/yacmo/yacmo.co.jp/public_html/wp-content/themes/yacmo/single-achievements.php on line 24
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /home/yacmo/yacmo.co.jp/public_html/wp-includes/media.php on line 1763
In the third-floor office, the floor shakes when cars pass by on the road in front of the building, causing a problem. To counteract this vibration, we installed "Floor Mate," an ultra-thin vibration control device that works just by placing it on the floor, and improved the floor swaying caused by traffic vibration to a level suitable for office use without requiring large-scale construction work.
Issues in this case study
The subject building is a steel-frame structure (3 floors above ground, 2 floors below ground) and is located along a major road. Vibrations are generated when vehicles pass by on the road and are transmitted to the building through the ground (Figure 1). Especially during times when many vehicles pass by, the third-floor office floor experiences a maximum of 7.2 [cm/s2] of shaking was occurring. As a result, a resident on the third floor said, "I can't concentrate on my work because the floor won't stop shaking." I can't concentrate on my work.
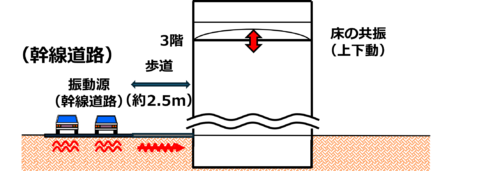
Figure 1: Location of the subject building
In preliminary measurements, accelerometer sensors were installed at the site boundary on the first floor and at the center of the floor on the third floor to measure vibration. As a result, it was confirmed that the vibration at the center of the third floor was greatly amplified around 16.7 [Hz] compared to the first floor site boundary (Figure 2).
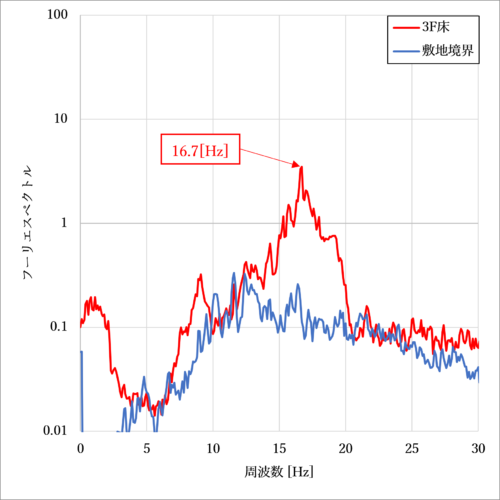
Figure 2: Traffic vibration FFT analysis results
At the same time, the natural frequency of the third floor was measured using heel impact excitation, as shown in Figure 3, and found to be predominant at 16.7 [Hz] (Figure 4).
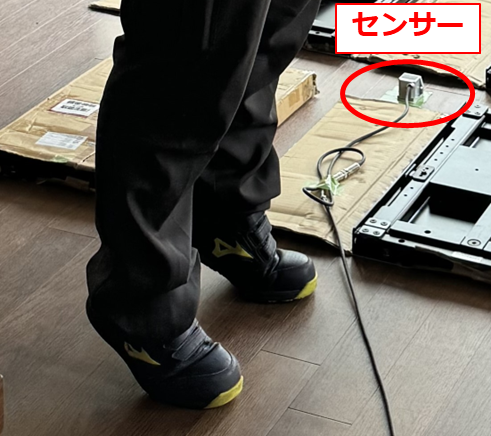

Figure 3. heel excitation measurement
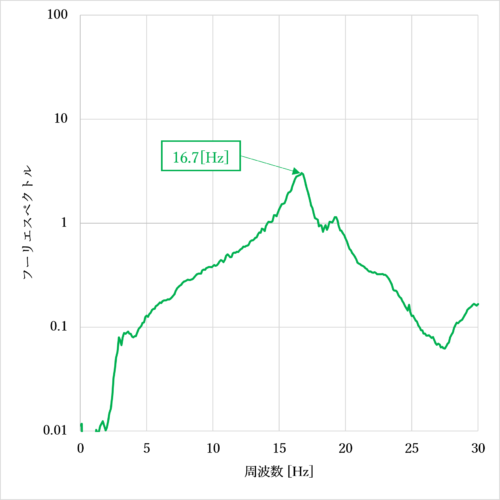
Figure 4. 3rd floor FFT analysis results for heel excitation
As a result of this measurement, it was determined that the vibration was likely amplified due to resonance.
In the case of amplification of vibration due to resonance, countermeasures by means of a vibration control device (Tuned Mass Damper) are considered effective.
However, since this case was an existing building with another tenant occupying the second floor, the following conditions were required
- Measures that do not require large-scale construction are desirable.
- If installed on the third floor, a small device that is not too obtrusive in space is desirable.
Based on the above points, we proposed our ultra-thin vibration-damping device, Floormate.
Details of Measures
The Tuned Mass Damper generates vibration with a 90-degree phase delay in response to floor vibration and uses the reaction force as damping force to suppress the amplitude of resonance. The Floormate features a compact design with a height of 44 [mm], a height of 560 [mm], and a width of 400 [mm], allowing it to be installed in tight spaces such as under OA floors. In addition, the total weight of the device is 35 [kg], making it lightweight and easy to install. Figure 5 shows the appearance of the Floor Mate.
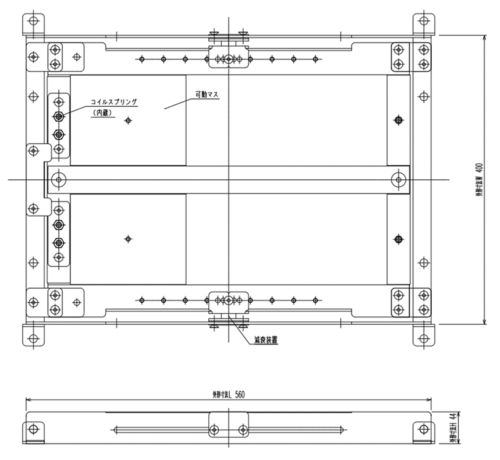
Figure 5: Exterior view of Floor Mate
The natural frequency and damping ratio can be changed by adjusting the position of the movable mass and the position of the damping device. The specifications of the device are as follows
| Vibration frequency adjustment range | Approx. 5 to 15 [Hz] (special specification for 16.7 [Hz] this time) |
| mass mass | 30 [kg]. |
| Gross mass of equipment | 35 [kg]. |
| Damping ratio adjustment range | Approx. 2-10 [% |

Figure 6: Floormate temporary installation diagram
As shown in Figure 6, the Floor Mate was temporarily installed and vibration acceleration was measured with the vibration control function on and off to evaluate the occupancy performance of the building in accordance with the Environmental Standard of the Architectural Institute of Japan (AIJES-V001-2018).
result
Traffic vibration was measured with the floor mate's vibration control function ON and OFF, and the effects of the vibration control measures are shown in Figure 7.
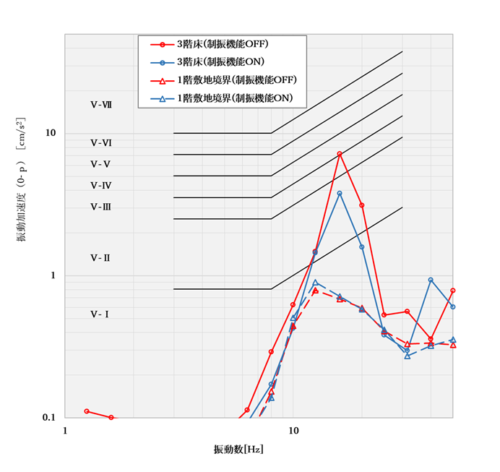
Figure 7: Vibration control effect of Floor Mate Comparison of floor acceleration when a vehicle passes by
When actual traffic vibration is used for measurement, it is difficult to compare the vibration control effect with traffic vibration of exactly the same excitation force. However, since the vibration acceleration at the site boundary is almost the same, it can be judged that the input excitation force is the same whether the vibration control function is turned on or off. On top of that, the vibration of the third floor is 7.2[cm/s2] to 3.8[cm/s2), confirming that the number of such products has been reduced to roughly one-half of the previous level.
Table 1.Description of evaluation levels for vertical vibration
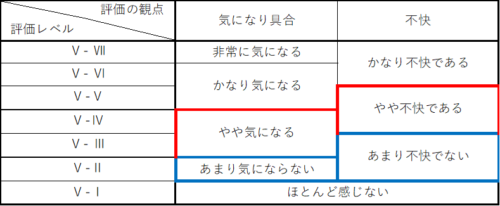
When we evaluated the occupant performance, the evaluation level went from "on the line between V-IV and V-III" to "V-II area," and the degree of bother/comfort improved from "somewhat bothersome/slightly uncomfortable/not very uncomfortable" to "not very bothersome/not very uncomfortable," confirming that the vibration control system is functioning effectively It was confirmed that the vibration control system was functioning effectively.
After that, we temporarily installed the system for about a week and tested its effects on residents, who commented that they felt less vibration, so we decided to install the system in its current location.

Figure 8: Floormate main installation
Related Pages
- Traffic vibration from the highway was transmitted to the office! Vibration Damping Devices to Countermeasure Later!
- Solving traffic vibration problems in detached houses!
- AMD vs TMD In-depth Comparison
- Product Information Floor Mate
