elastic wave
When an external force is applied, a change in volume and shape proportional to the magnitude of the force is produced, and when the external force is removed, the solid returns to its original shape.
Elastic waves can be divided into volume waves with volume change and isovolumetric waves, which cause shape change but no volume change, and waves oscillating parallel to the direction of wave motion are called longitudinal waves (primary waves (P waves), compressional waves, sparse waves, etc.), while waves oscillating perpendicular to the direction of wave motion are transverse waves (secondary waves (S waves, shear waves, etc.)), Secondary wave (S-wave), shear wave, etc.).
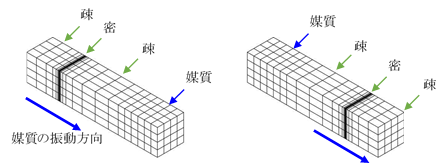
Figure Vertical Wave
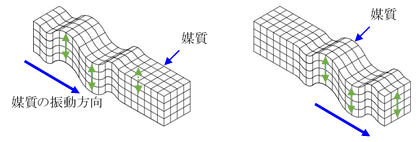
figure (diagram) horizontal wave
In ground vibrations and other phenomena, resistance to volume change is the cause of longitudinal waves, while resistance to shape change is the cause of transverse waves. Longitudinal waves propagate faster than transverse waves.
Two types of waves, longitudinal and transverse, propagate in an elastic body at infinity and are called entity waves.
On the other hand, in the case of a semi-infinite medium such as the ground, which is elastic only below the surface of the ground, the waves that propagate mainly along the surface of the medium are called surface waves, the most typical of which are called Rayleigh waves (R waves).
Other types of surface waves occur when there is a soft surface layer on a hard foundation, called rub waves.
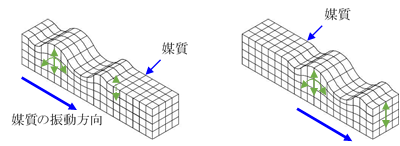
(1) Rayleigh wave
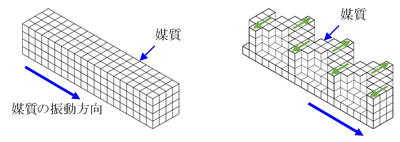
(2) Love Wave
These waves can be organized as follows.
| entity wave | Longitudinal waves (primary waves (P waves), compressional waves, sparse dense waves, approximate 5-7 km/s during earthquake) |
| Transverse waves (secondary waves (S-waves), shear waves, approx. 3-4 km/s during earthquake)note (supplementary information) symbol) | |
| surface wave | Rayleigh wave (R-wave) |
| Love Wave |
In a layer a little closer to the ground surface (top of the engineering base), etc., it is several hundred m/s. Vibrations seen in ground measurements, etc., are often a composite of the above waves.
sound wave
Sound waves are a type of elastic wave, but since air is the medium for most of them, they are only longitudinal waves with sparse oscillatory propagation.
*References
New Pollution Prevention Technology and Laws and Regulations 2016 Noise and Vibration Edition Pollution Prevention Technology and Laws and Regulations Editorial Board, ed.
