Engineering Group, Division 1
Haruki Fukatsu
In recent years, an increasing number of factories have been installing new machinery or changing the layout of their equipment as a result of capital investment. These changes can lead to two unexpected problems: first, noise, and second, vibration. Noise problems are easy to perceive and relatively easy to counter by enclosing the machinery, but vibration problems are difficult to perceive and in some cases can be aggravated, making it difficult to know how to counteract the problem. Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
Therefore, we will pick up and explain the vibration countermeasure method.
1. vibration in the factory
As installed machinery increases in output and speed, large floor shaking is becoming a problem in an increasing number of cases. Vibration problems in factories can be divided into two major categories: first, the impact on workers, and second, the impact on surrounding machinery.
The “impact on workers” refers to the deterioration of the work environment. Not only psychological discomfort, but also reduced work efficiency and increased errors can result.
Vibration affects surrounding machinery” is a problem in which vibration degrades the performance of machinery. Vibration-sensitive machines (vibration-insensitive machines) include inspection equipment (optical microscopes and X-ray CT scanning equipment), precision processing machines (grinders and multi-axis processing machines), mounting machines (chip mounters), and semiconductor lithography equipment. When vibration affects the defect rate or accuracy, it is required to reduce the influence of vibration from surrounding machines.


2. What are the actual vibration countermeasures?
Countermeasures are implemented by disconnecting the machine from its surroundings. There are two types of measures: anti-vibration measures to suppress vibrations transmitted externally from machines that generate vibrations, and vibration-isolation measures to suppress the effects of external vibrations on machines that are vulnerable to vibrations.
For both vibration isolation and vibration elimination, there are two types of measures: one is to support only the machine with elastic materials (edge trimming) as shown on the left side of Figure 3, and the other is to support the floor supporting the machine with elastic materials (edge trimming) as shown on the right side of Figure 3 for higher vibration reduction effect. In this case, the amount of vibration reduction depends on the softness of the elastic material used for vibration isolation or vibration elimination. Generally, the softer the elastic body, the more effective the vibration reduction tends to be.
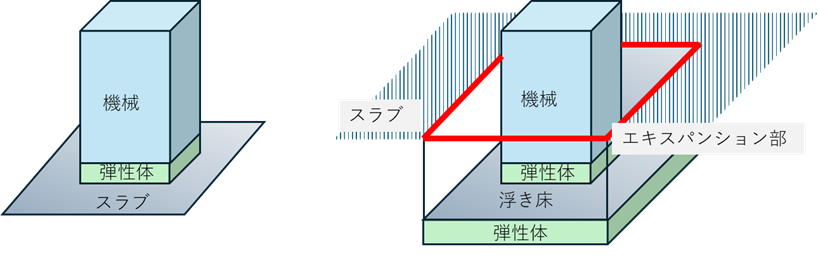
Figure 3: Example of vibration countermeasures

Figure 4: Examples of elastic materials used for countermeasures
