noise
From a physical point of view, sound refers to air vibrations (waves), and noise is a general term for undesirable sounds or sounds that are better off without.
As a feature of this issue,
- The definition is vague and its judgment is subjective.
- Problems are localized and multiple.
- Leaves no environmentally polluting materials to be processed.
There are
Noise is defined by the government as a form of pollution. There are several types of noise, such as factory noise, construction noise, road traffic noise, aircraft noise, and railroad noise, for which standards are set by law.
However, there are many cases that do not fit into a uniform law, making this issue more difficult.
Noise Level
Generally, noise evaluation is expressed in terms of the sound pressure level (dB), which is a physical quantity, weighted by the frequency correction characteristic (A characteristic), which is considered to be close to human perception.
The graph below shows the A characteristic and the flat (unweighted) characteristic.
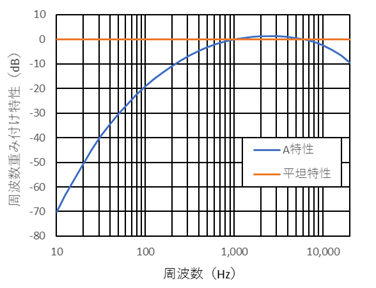
Figure Frequency Weighting Characteristics
Approximate noise level
| Noise Level (dB) | Assumed location |
| 80-90 | Inside pachinko parlors and game arcades |
| 70 to 80 | In airplanes, on trains, around major highways, the sound of cicadas |
| 60 to 70 | On board Shinkansen bullet trains, buses, and coffee shops Inside a family restaurant |
| 50-60 | Around bank counters, in museums, around government office counters, in bookstores |
| 40 to 50 | High-rise residential area (daytime), quiet office, cemetery (daytime), in museum Detached residential area (daytime), in library |
| 30 to 40 | High-rise residential area (at night), detached residential area (at night), hotel rooms |
(Noise level, for urban and suburban areas)
*References
New Pollution Prevention Technology and Laws and Regulations 2016 Noise and Vibration Edition Pollution Prevention Technology and Laws and Regulations Editorial Board, ed.
