Air and solid sound
There are two types of sound propagation: airborne sound, which is transmitted (and heard) by vibrating air from a sound source, and solid-state sound, which is transmitted by vibrations transmitted through structural materials that shake the air at another location.
Children, etc. in a housing complex are compared to a sound source,
(1) I hear the cries and screams of an infant from the floor above my room. ⇒airborne noise
(2) I hear a sound as if someone jumped from the ceiling of the room. ⇒solid-state propagation noise
will be.
(In the case of (1), air-borne sound can be effectively addressed by improving the sound insulation performance of walls and ceilings, but in the case of (2), solid-borne sound, which is caused by vibration transmitted through the building frame, the amount of vibration transmitted to the building frame must be reduced to be effective. Therefore, vibration isolation measures, such as vibration isolation of the upper floor and suspension of the walls and ceilings of the lower floor, are necessary.
Thus, to solve noise problems, it is important to understand the phenomenon well and to choose the appropriate countermeasures for each.
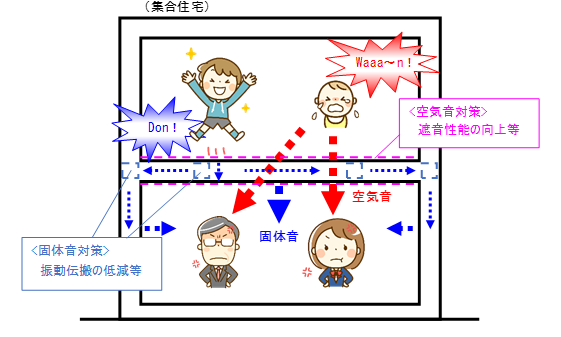
Fig. Image of airborne and individually propagated sound generation in a housing complex
