This section provides an easy-to-understand explanation of sound absorption and sound insulation performance, which are the basics of noise control methods.
Sound absorption performance and characteristics of sound absorbing materials
Sound absorption is a phenomenon in which sound is converted into thermal energy by a material. Noise is reduced by decreasing sound energy. Materials suitable for sound absorption are called sound-absorbing materials.
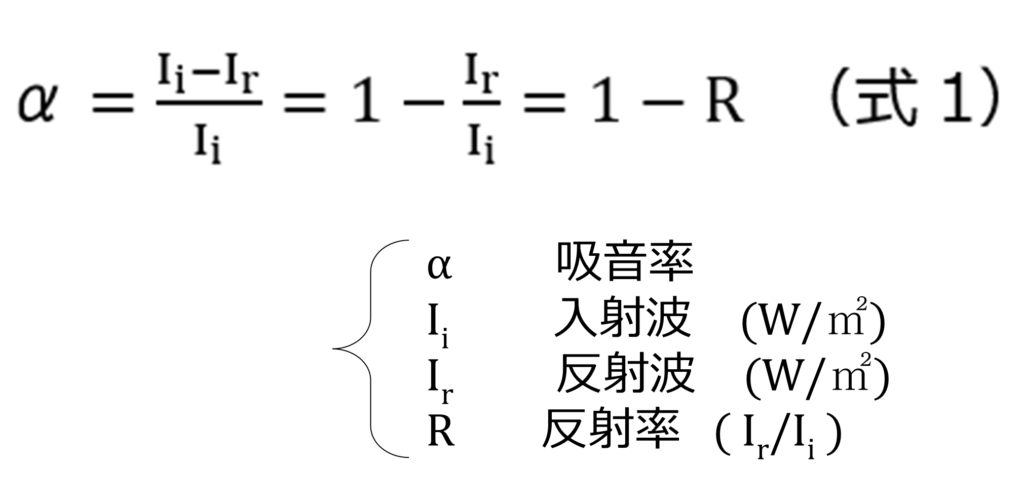
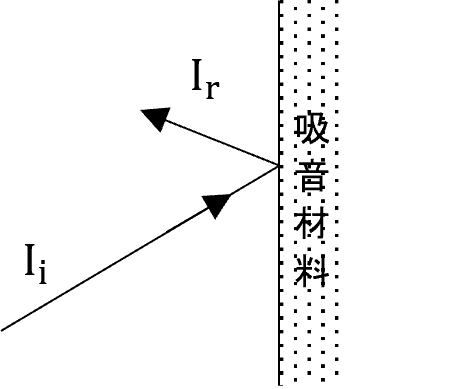
The performance of a sound absorbing material is expressed in terms of sound absorption coefficient per frequency. The sound absorption coefficient α is expressed as the ratio of the energy of sound incident on the material to the energy of sound not reflected back (Equation 1, Figure 1). Therefore, α is a value between 0 and 1. The closer the value is to 1, the higher the sound absorption performance.
The sound absorption coefficient α of incident sound from any direction is generally measured by the sound absorption coefficient measured by JIS A 1409: 1998 "Measurement method of sound absorption coefficient by reverberation room method".
Also, as can be seen from (Equation 1), if no reflections are returned, the sound absorption coefficient is 1. In other words, apertures can be regarded as having a sound absorption coefficient of 1.
Types of Sound Absorbing Materials
Sound absorbing materials can be divided into three main types according to their sound absorption mechanism.
Porous sound-absorbing material
Porous means a sponge-like material with many small pores. When sound enters these bubbles, friction and vibration cause some of the sound to be converted into thermal energy. Thickening the sound-absorbing material or adding a layer of air behind it will increase its sound-absorbing performance.Generally excellent at absorbing high frequency sound.
Plate (membrane) vibration type sound absorbing material
When sound strikes a material such as plywood or canvas, vibration is created in the board or membrane. The internal friction caused by the vibration consumes some of the sound energy.Generally absorbs low frequency sound, but its sound absorption rate is not so good.
Resonator type sound absorber
For sounds in the frequency band close to the resonance frequency of the resonator, the area around the hole vibrates violently, and sound energy is consumed as frictional heat.Generally, high sound absorption coefficient can be obtained only near the resonance frequency.
Sound absorbing materials used as building materials are either of these three types or a combination of them. By selecting a sound-absorbing material according to the frequency characteristics of the sound you want to absorb, you can achieve the appropriate effect.
How to determine sound insulation performance and transmission loss
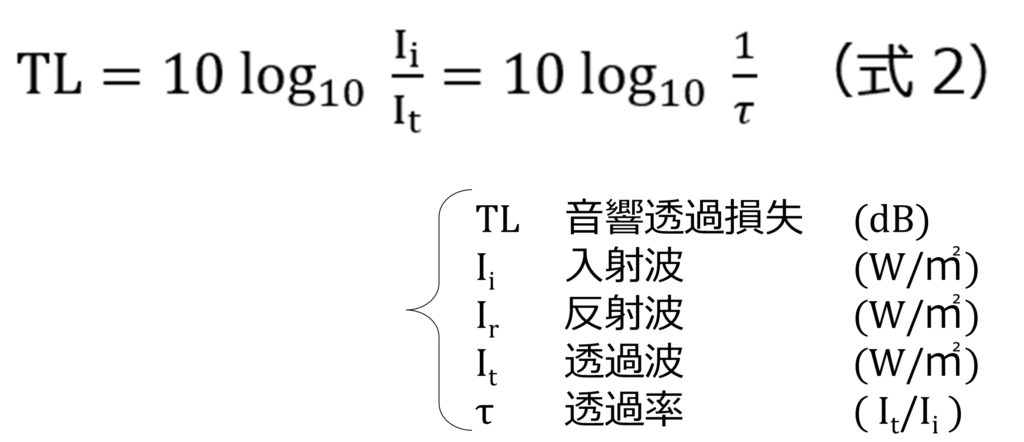
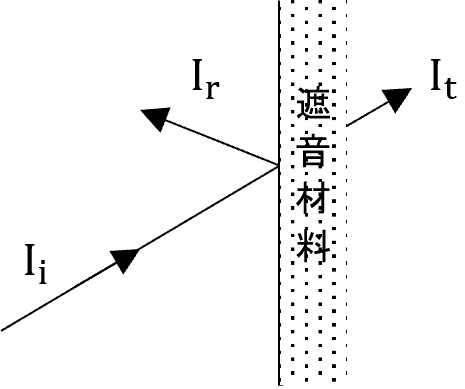
Sound insulation is the process of blocking the propagation of sound by means of a material, and the material to be blocked is called a sound insulation material. The performance is expressed as sound transmission loss TL (dB) per frequency based on the sound transmission coefficient τ (ratio of the energy of incident sound to that of transmitted sound through the material) (Equation 2, Figure 2). Sound transmission loss (TL), like sound absorption coefficient (α), depends on the incident sound conditions on the material, so the TL for incident sound from any direction is generally obtained from the measurement specified in JISA1416:2000 "Methods of measuring airborne sound insulation performance of building components in the laboratory.
Transmission loss by mass law
For single-layer (one-layer) walls, another method is to determine the sound transmission loss (TL) for incident sound (turbulent incident) from any direction by the practical mass law equation shown in Equation 3.

Combination effect of sound insulation and sound absorption materials
A common measure in construction is to surround the sound source with sound insulation material. By enclosing the sound source, the sound inside becomes denser and louder. In this case, combining sound-absorbing materials inside the enclosure can reduce the increase of the inner sound. By combining sound absorbing and sound insulation materials, effective noise reduction measures can be taken.
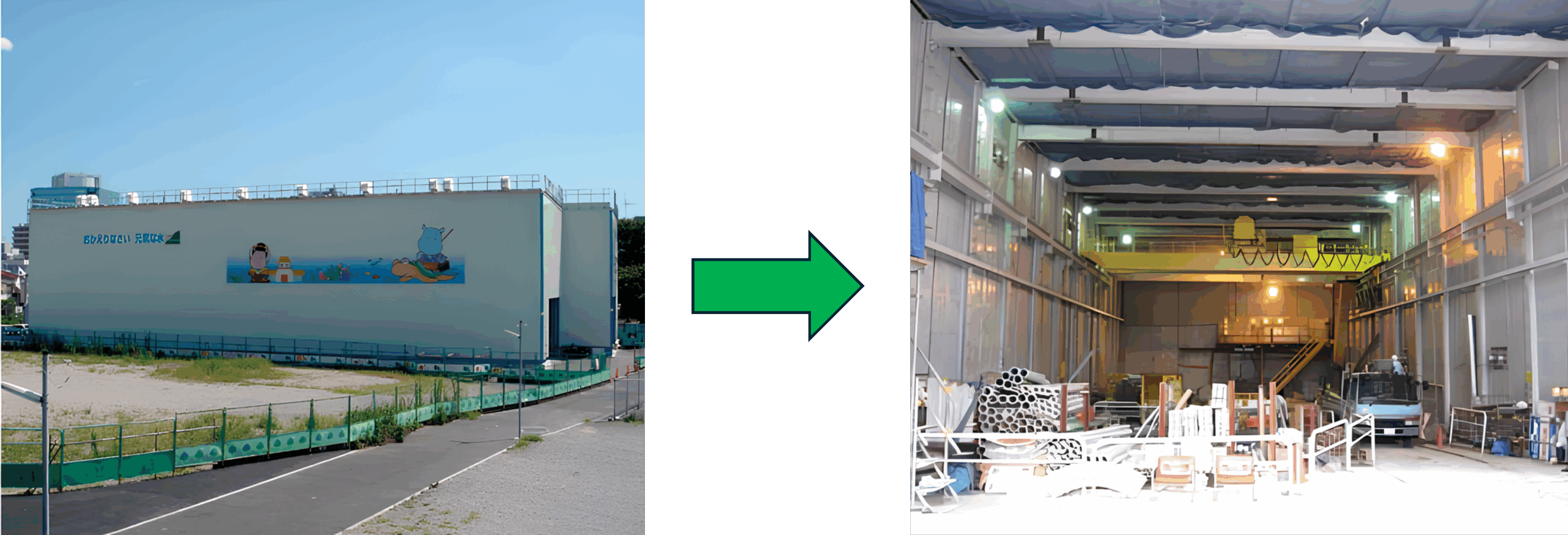
Example of noise reduction by sound absorption and sound insulation (soundproof house)
Here are some examples of noise reduction measures using sound absorption and sound insulation materials. At construction sites, there are machines and vehicles that generate loud noise. By enclosing the machines, which are the source of noise, with panels made of sound-absorbing or sound-insulating materials, it is possible to prevent the sound inside from being transmitted outside. A soundproof box or a large building size is called a soundproof house (Figure 3).
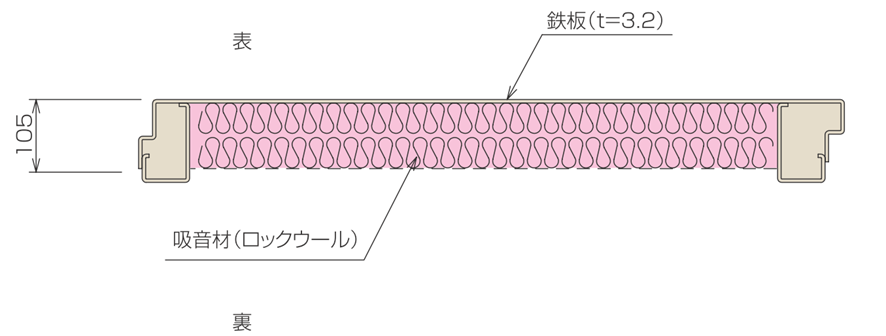
Structure of soundproofing panels (sound insulation and sound absorption)
Soundproofing panels (Figure 4), which combine steel plates for sound insulation and rock wool for sound absorption, are used as wall and ceiling materials to provide high soundproofing performance.
For information on soundproofing panels and other products, please contactthis way (direction close to the speaker or towards the speaker)for more information.
References
New Pollution Prevention Techniques and Laws 2025 Noise and Vibration Edition Pollution Prevention Techniques and Laws Editorial Board